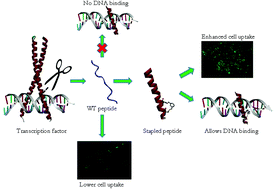
Stapling monomeric GCN4 peptides allows for DNA binding and enhanced cellular uptake†
Abstract
The basic DNA recognition region of the GCN4 protein comprising 23 amino acids has been modified to contain two optimally positioned cysteines which have been linked and stapled using cross-linkers of suitable lengths. This results in stapled peptides with a stabilized α-helical conformation which allows for DNA binding and concurrent enhancement of cellular uptake.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...