Ion transport and selectivity in biomimetic nanopores with pH-tunable zwitterionic polyelectrolyte brushes
Abstract
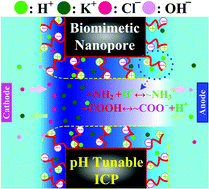
Inspired by nature, functionalized nanopores with biomimetic structures have attracted growing interests in using them as novel platforms for applications of regulating ion and nanoparticle transport. To improve these emerging applications, we study theoretically for the first time the ion transport and selectivity in short nanopores functionalized with pH tunable, zwitterionic polyelectrolyte (PE) brushes. In addition to background salt ions, the study takes into account the presence of H+ and OH− ions along with the chemistry reactions between functional groups on PE chains and protons. Due to ion concentration polarization, the charge density of PE layers is not homogeneously distributed and depends significantly on the background salt concentration, pH, grafting density of PE chains, and applied voltage bias, thereby resulting in many interesting and unexpected ion transport phenomena in the nanopore. For example, the ion selectivity of the biomimetic nanopore can be regulated from anion-selective (cation-selective) to cation-selective (anion-selective) by diminishing (raising) the solution pH when a sufficiently small grafting density of PE chains, large voltage bias, and low background salt concentration are applied.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...