Highly sensitive detection of DNA methylation levels by using a quantum dot-based FRET method†
Abstract
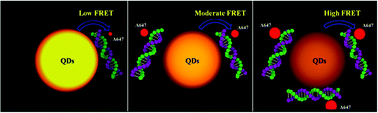
DNA methylation is the most frequently studied epigenetic modification that is strongly involved in genomic stability and cellular plasticity. Aberrant changes in DNA methylation status are ubiquitous in human cancer and the detection of these changes can be informative for cancer diagnosis. Herein, we reported a facile quantum dot-based (QD-based) fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) technique for the detection of DNA methylation. The method relies on methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes for the differential digestion of genomic DNA based on its methylation status. Digested DNA is then subjected to PCR amplification for the incorporation of Alexa Fluor-647 (A647) fluorophores. DNA methylation levels can be detected qualitatively through gel analysis and quantitatively by the signal amplification from QDs to A647 during FRET. Furthermore, the methylation levels of three tumor suppressor genes, PCDHGB6, HOXA9 and RASSF1A, in 20 lung adenocarcinoma and 20 corresponding adjacent nontumorous tissue (NT) samples were measured to verify the feasibility of the QD-based FRET method and a high sensitivity for cancer detection (up to 90%) was achieved. Our QD-based FRET method is a convenient, continuous and high-throughput method, and is expected to be an alternative for detecting DNA methylation as a biomarker for certain human cancers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...