Insulin-coated gold nanoparticles as a new concept for personalized and adjustable glucose regulation
Abstract
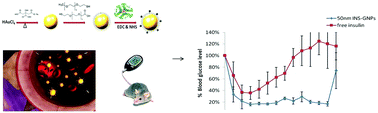
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disease, characterized by high blood glucose levels, affecting millions of people around the world. Currently, the main treatment for diabetes requires multiple daily injections of insulin and self-monitoring of blood glucose levels, which markedly affect patients’ quality of life. In this study we present a novel strategy for controlled and prolonged glucose regulation, based on the administration of insulin-coated gold nanoparticles (INS-GNPs). We show that both intravenous and subcutaneous injection of INS-GNPs into a mouse model of type 1 diabetes decreases blood glucose levels for periods over 3 times longer than free insulin. We further showed that conjugation of insulin to GNPs prevented its rapid degradation by the insulin-degrading-enzyme, and thus allows controlled and adjustable bio-activity. Moreover, we assessed different sizes and concentrations of INS-GNPs, and found that both parameters have a critical effect in vivo, enabling specific adjustment of blood glucose levels. These findings have the potential to improve patient compliance in diabetes mellitus.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...