Multilayered silicene: the bottom-up approach for a weakly relaxed Si(111) with Dirac surface states†
Abstract
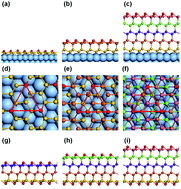
Combining first principles investigations and scanning tunneling microscopy, we identify that the presumable van der Waals packed multilayered silicene sheets spontaneously transform into a diamond-structure bulk Si film due to strong interlayer couplings. In contrast to drastic surface reconstruction on conventional Si(111), multilayered silicene prepared by bottom-up epitaxy on Ag(111) exhibits a nearly ideal flat surface with only weak buckling. Without invoking Ag surfactants, √3 × √3 honeycomb patterns emerge thanks to dynamic fluctuation of mirror-symmetric rhombic phases, similar to monolayered silicene [Chen et al., Phys. Rev. Lett., 2013, 110, 085504]. The weak relaxation enables novel surface states with a Dirac linear dispersion.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...