Kelvin probe imaging of photo-injected electrons in metal oxide nanosheets from metal sulfide quantum dots under remote photochromic coloration†
Abstract
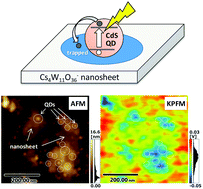
Metal oxide and quantum dot (QD) heterostructures have attracted considerable recent attention as materials for developing efficient solar cells, photocatalysts, and display devices, thus nanoscale imaging of trapped electrons in these heterostructures provides important insight for developing efficient devices. In the present study, Kelvin probe force microscopy (KPFM) of CdS quantum dot (QD)-grafted Cs4W11O362− nanosheets was performed before and after visible-light irradiation. After visible-light excitation of the CdS QDs, the Cs4W11O362− nanosheet surface exhibited a decreased work function in the vicinity of the junction with CdS QDs, even though the Cs4W11O362− nanosheet did not absorb visible light. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy revealed that W5+ species were formed in the nanosheet after visible-light irradiation. These results demonstrated that excited electrons in the CdS QDs were injected and trapped in the Cs4W11O362− nanosheet to form color centers. Further, the CdS QDs and Cs4W11O362− nanosheet composite films exhibited efficient remote photochromic coloration, which was attributed to the quantum nanostructure of the film. Notably, the responsive wavelength of the material is tunable by adjusting the size of QDs, and the decoloration rate is highly efficient, as the required length for trapped electrons to diffuse into the nanosheet surface is very short owing to its nanoscale thickness. The unique properties of this photochromic device make it suitable for display or memory applications. In addition, the methodology described in the present study for nanoscale imaging is expected to aid in the understanding of electron transport and trapping processes in metal oxide and metal chalcogenide heterostructure, which are crucial phenomena in QD-based solar cells and/or photocatalytic water-splitting systems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...