High-performance graphene/sulphur electrodes for flexible Li-ion batteries using the low-temperature spraying method†
Abstract
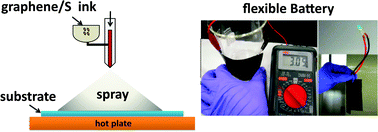
Elementary sulphur (S) has been shown to be an excellent cathode material in energy storage devices such as Li–S batteries owing to its very high capacity. The major challenges associated with the sulphur cathodes are structural degradation, poor cycling performance and instability of the solid–electrolyte interphase caused by the dissolution of polysulfides during cycling. Tremendous efforts made by others have demonstrated that encapsulation of S materials improves their cycling performance. To make this approach practical for large scale applications, the use of low-cost technology and materials has become a crucial and new focus of S-based Li-ion batteries. Herein, we propose to use a low temperature spraying process to fabricate graphene/S electrode material, where the ink is composed of graphene flakes and the micron-sized S particles prepared by grinding of low-cost S powders. The S particles are found to be well hosted by highly conductive graphene flakes and consequently superior cyclability (∼70% capacity retention after 250 cycles), good coulombic efficiency (∼98%) and high capacity (∼1500 mA h g−1) are obtained. The proposed approach does not require high temperature annealing or baking; hence, another great advantage is to make flexible Li-ion batteries. We have also demonstrated two types of flexible batteries using sprayed graphene/S electrodes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...