Surface plasmon coupled metal enhanced spectral and charge transport properties of poly(3,3′′′-dialkylquarterthiophene) Langmuir Schaefer films†
Abstract
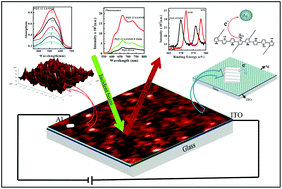
The coupling of organic molecule excitons with metal nano-structure surface plasmons can improve the performance of optoelectronic devices. This paper presents the effect of localized silver metal surface plasmons on spectral as well as charge transport properties of ordered molecular Langmuir Schaefer (LS) films of a fluorescent conducting multifunctional organic polymer: poly (3,3′′′-dialkylquarterthiophene) [PQT-12]. The stability and thickness of the PQT-12 LS film were studied by the pressure vs. area isotherm curve. Atomic force microscopy images indicate the formation of a smooth ordered polymer thin LS film of PQT-12 over silver nanostructure island films [SNIF] (∼40 to 50 nm in size). Raman, electronic absorption and fluorescence spectral measurements of the PQT-12 LS film, near SNIF i.e. the near field, show a plasmon coupled enhancement of ∼13 fold in the intensity of Raman bands along with a two-fold enhancement in the absorption band (531 nm) and a six-fold enhancement in the fluorescence band (665 nm) coupled with a decrease in fluorescence decay time with improved photostability as compared to an identical control sample containing no SNIF i.e. the far field condition. These results indicate the formation of a plasmon coupled unified fluorophore system due to adsorption of the PQT-12 LS film over SNIF. The effect of plasmonic coupling is also studied by applying an electric field in sandwiched structures of Al/PQT-12 LS/SNIF/ITO with respect to Al/PQT-12 LS/ITO. Nearly three orders of magnitude enhancement in the current density (J–V plot) of the PQT-12 LS film is observed in the presence of SNIF, which further increases, on illuminating the film by green laser light [532 nm], while the fluorescence intensity and decay time decrease. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic measurements of SNIF also show a red shift in 3d3/2 and 3d5/2 transitions of silver in the PQT-12 coated LS film, which indicates partial charge transfer from the PQT-12 polymer backbone to SNIF and causes an enhancement in conductivity. This again supports the formation of a field controlled radiating plasmon coupled fluorophore unified system. These findings show greater potential in developing a voltage controlled high photon flux electroluminescent material for multifarious applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...