Personalized disease-specific protein corona influences the therapeutic impact of graphene oxide†
Abstract
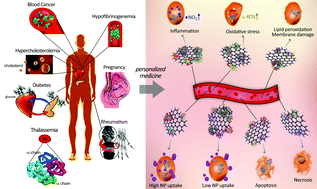
The hard corona, the protein shell that is strongly attached to the surface of nano-objects in biological fluids, is recognized as the first layer that interacts with biological objects (e.g., cells and tissues). The decoration of the hard corona (i.e., the type, amount, and conformation of the attached proteins) can define the biological fate of the nanomaterial. Recent developments have revealed that corona decoration strongly depends on the type of disease in human patients from which the plasma is obtained as a protein source for corona formation (referred to as the ‘personalized protein corona’). In this study, we demonstrate that graphene oxide (GO) sheets can trigger different biological responses in the presence of coronas obtained from various types of diseases. GO sheets were incubated with plasma from human subjects with different diseases/conditions, including hypofibrinogenemia, blood cancer, thalassemia major, thalassemia minor, rheumatism, fauvism, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes, and pregnancy. Identical sheets coated with varying protein corona decorations exhibited significantly different cellular toxicity, apoptosis, and uptake, reactive oxygen species production, lipid peroxidation and nitrogen oxide levels. The results of this report will help researchers design efficient and safe, patient-specific nano biomaterials in a disease type-specific manner for clinical and biological applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...