Efficient inorganic solid solar cells composed of perovskite and PbS quantum dots†
Abstract
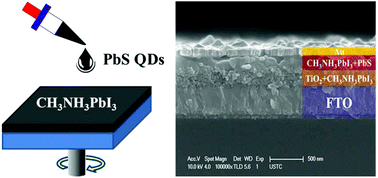
Lead halide perovskite solar cells have attracted great interest due to their high efficiency and simple fabrication process. However, the high efficiency heavily relies on expensive organic hole-transporting materials (OHTMs) such as 2,2′,7,7′-tetrakis(N,N-di-p-methoxyphenylamine)-9,9′-spirobifluorene (spiro-MeOTAD), it is preferable to replace these expensive OHTMs by inorganic and low cost materials. Here, we report colloidal PbS quantum dots synthesized by a facile method and used as the inorganic hole-transporting material in a hybrid perovskite solar cell. By controlling the crystalline morphology of the perovskite capping layer, the recombination process is significantly retarded. Furthermore, a pure inorganic solar cell prepared by a two-step process demonstrated a nearly 8% power conversion efficiency due to efficient charge separation by a cascade of junctions and retarding charge recombination by a void-free capping layer. The stability of the inorganic solar cell was also tested with a little decay observed within ca. 100 h.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...