Reduced ceria nanofilms from structure prediction†
Abstract
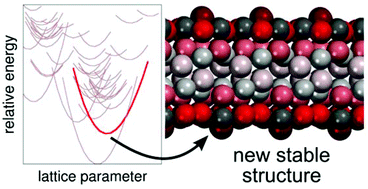
Experimentally, Ce2O3 films are used to study cerium oxide in its fully or partially reduced state, as present in many applications. We have explored the space of low energy Ce2O3 nanofilms using structure prediction and density functional calculations, yielding more than 30 distinct nanofilm structures. First, our results help to rationalize the roles of thermodynamics and kinetics in the preparation of reduced ceria nanofilms with different bulk crystalline structures (e.g. A-type or bixbyite) depending on the support used. Second, we predict a novel, as yet experimentally unresolved, nanofilm which has a structure that does not correspond to any previously reported bulk A2B3 phase and which has an energetic stability between that of A-type and bixbyite. To assist identification and fabrication of this new Ce2O3 nanofilm we calculate some observable properties and propose supports for its epitaxial growth.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...