Simultaneous direct detection of Shiga-toxin producing Escherichia coli (STEC) strains by optical biosensing with oligonucleotide-functionalized gold nanoparticles†
Abstract
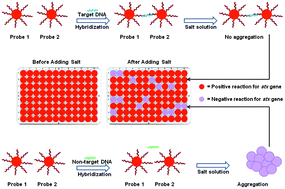
A simultaneous direct detection of Shiga-toxin producing strains of E. coli (STEC; “Big Six” – O26, O45, O103, O111, O121, and O145) as well as O157 strains by optical biosensing with oligonucleotide-functionalized gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) was developed. Initially, conserved regions of stx genes were amplified by asymmetric polymerase chain reaction (asPCR). Pairs of single stranded thiol-modified oligonucleotides (30-mer) were immobilized onto AuNPs and used as probes to capture regions of stx1 (119-bp) and/or stx2 (104-bp) genes from STEC strains. DNA samples from pure cultures and food samples were sandwich hybridized with AuNP-oligo probes at optimal conditions (50 °C, 30 min). A complex was formed from the hybridization of AuNP-probes and target DNA fragments that retained the initial red color of the reaction solutions. For non-target DNA, a color change from red to purplish-blue was observed following an increase in salt concentration, thus providing the basis of simultaneous direct colorimetric detection of target DNA in the samples. Enrichment and pooling systems were incorporated to efficiently process a large number of food samples (ground beef and blueberries) and detection of live targets. The detection limit was <1 log CFU g−1, requiring less than 1 h to complete after DNA sample preparation with 100% specificity. Gel electrophoresis verified AuNP-DNA hybridization while spectrophotometric data and transmission electron microscope (TEM) images supported color discrimination based on the occurrence of molecular aggregation. In conclusion, the significant features of this approach took advantage of the unique colorimetric properties of AuNPs as a low-cost and simple approach yet with high specificity for simultaneous detection of STEC strains.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...