Targeting FR-expressing cells in ovarian cancer with Fab-functionalized nanoparticles: a full study to provide the proof of principle from in vitro to in vivo†
Abstract
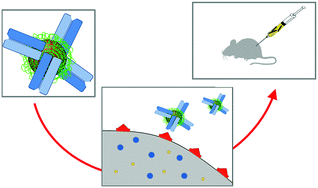
Efficient targeting in tumor therapies is still an open issue: systemic biodistribution and poor specific accumulation of drugs weaken efficacy of treatments. Engineered nanoparticles are expected to bring benefits by allowing specific delivery of drug to the tumor or acting themselves as localized therapeutic agents. In this study we have targeted epithelial ovarian cancer with inorganic nanoparticles conjugated to a human antibody fragment against the folate receptor over-expressed on cancer cells. The conjugation approach is generally applicable. Indeed several types of nanoparticles (either magnetic or fluorescent) were engineered with the fragment, and their biological activity was preserved as demonstrated by biochemical methods in vitro. In vivo studies with mice bearing orthotopic and subcutaneous tumors were performed. Elemental and histological analyses showed that the conjugated magnetic nanoparticles accumulated specifically and were retained at tumor sites longer than the non-conjugated nanoparticles.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...