FTIR, magnetic and Mössbauer investigations of nano-crystalline FexCo1−x (0.4 ≤ x ≤ 0.8) alloys synthesized via a superhydride reduction route
Abstract
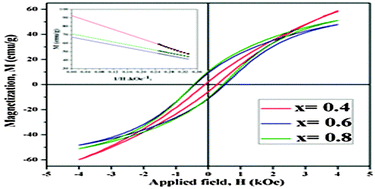
The present investigation reveals the synthesis of capped nano-crystalline FexCo1−x (0.2 ≤ x ≤ 0.8) alloys via a superhydride reduction route using oleic acid and oleylamine as stabilizing agents. The synthesized nano-particles are stable against oxidation in an air atmosphere (air stable) at room temperature (298 K). The structure–property correlation in FeCo alloys has been achieved using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), magnetic and Mössbauer measurements. A FTIR study indicates the presence of organic content at the surface of the nanoparticles, which helps in the stabilization of the FeCo samples in an air atmosphere. FeCo alloys crystallize in a pure α-phase with the increase in the values of lattice parameters with the increase in Fe content, i.e. 2.836(±4) Å, 2.852(±2) Å, 2.859(±1) Å and 2.868(±1) Å for x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6 and 0.8, respectively. Average crystallite sizes and TEM particle sizes were found to be in the range of ≈23–38 nm and 11–51 nm, respectively. The values of the saturation magnetization (Ms) for FeCo alloys range from 71.1–92.5 emu g−1 for heat treated materials and 93.1–142.2 emu g−1 after applying the corrections for organic wt% at the surface of the materials. The observed values of effective anisotropy constants (Keff) of FexCo1−x alloys from field cooled (FC) and zero field cooled (ZFC) studies (i.e. 1.5 kJ m−3, 4.6 kJ m−3 and 14.3 kJ m−3 for x = 0.4, 0.6 and 0.8, respectively) reveal the contribution from the reduced particle size and surface anisotropy. The maximum value of a hyperfine field for FexCo1−x alloys was found to be 34.9 T for Fe0.6Co0.4 composition and has been interpreted on the basis of enhancement of Fe moments in the disordered crystal lattice.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...