A novel cyclic non-ligand dual-cloud point extraction for the preconcentration of cadmium(ii) through pH regulation in food and environmental matrices†
Abstract
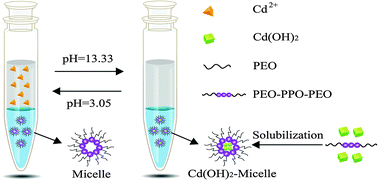
A new simple cyclic non-ligand dual-cloud point extraction (NL-DCPE) pretreatment method through pH regulation coupled with flame atomic absorption spectrometry (FAAS) for the analysis of trace cadmium(II) was developed. In NL-DCPE, the cloud point process was carried out twice. First, Cd(II) was extracted into the thermosensitive triblock copolymer L31-rich phase in the form of Cd(OH)2 at pH 13.33, leaving the hydrophilic impurities behind in the aqueous phase. Second, the hydroxide dissociated at pH 3.05 and Cd(II) was back-extracted into the aqueous phase in the form of Cd2+, thereby discarding the hydrophobic impurities in the L31-rich phase. The L31-rich phase was recycled, and the extraction efficiency could reach up to 90%. Under the optimum conditions, the preconcentration of a 10 mL sample solution could achieve an enrichment factor of 29 and an extraction efficiency of 96.3%. The relative standard deviation (RSD) for six replicate determinations was 4.5%. The method was applied to the determination of trace Cd(II) in food and environmental samples, and the range of recoveries were 90–102.5%. NL-DCPE successfully achieved the selective separation of the analytes and avoided the interference of the surfactant on the instrument analysis. This method had distinct advantages of simplicity, efficiency, economy and environmental protection, and also has great potential for the preconcentration and separation of other metal ions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...