A novel dual-functional fluorescent chemosensor for the selective detection of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene and Hg2+†
Abstract
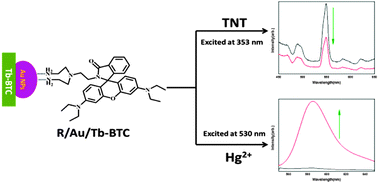
Herein we develop a dual-functional fluorescent chemosensor R/Au/Tb-BTC. This chemosensor was prepared by immobilizing rhodamine derivative probes (R) onto the surface of the metal–organic framework Tb-BTC via Au nanoparticles (Au NPs). The chemosensor was characterized by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and the UV-vis spectrum. R/Au/Tb-BTC was applied in the detection of nitroaromatic compounds and Hg2+, which were detected by Tb-BTC and R respectively. Nitroaromatic compounds, such as 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT), nitrobenzene (NB) and 4-nitrophenol (PNP), could reduce the fluorescence intensity of R/Au/Tb-BTC in ethanol solution. Thus R/Au/Tb-BTC can selectively and sensitively detect nitroaromatic compounds, especially TNT. Meanwhile, R/Au/Tb-BTC exhibits both fluorescence and colorimetric properties for the detection of Hg2+ in aqueous solution. It presents excellent anti-disturbance ability when exposed to a series of competitive cations such as Na+, K+, Ag+, Li+, Ba2+, Ca2+, Pb2+, Cd2+, Co2+, Cu2+, Mg2+, Mn2+, Ni2+, and Zn2+. More importantly, when TNT and Hg2+ coexist in ethanol solution, the two pollutants can be detected using one chemosensor R/Au/Tb-BTC.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...