Novel synthetic approach for 1,4-dihydroxyanthraquinone and the development of its lithiated salts as anode materials for aqueous rechargeable lithium-ion batteries
Abstract
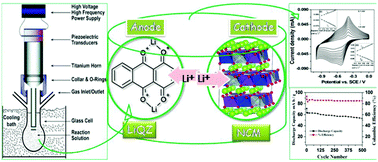
The use of organic electrode materials in the field of lithium ion batteries is becoming a keen interest for the present generation of scientists. Here we are reporting a novel method of synthesis for electrode materials using a combination of sono-chemical and thermal methods. The advantages of organic active materials in lithium ion batteries are of core interest in this study. Structural confirmations are provided by FT-IR, 1H NMR, MALDI-TOF mass spectroscopy and powder XRD data. The electrochemical properties of lithiated-1,4-dihydroxyanthraquinone were studied using electrochemical techniques such as cyclic voltammetry, galvanostatic cyclic potential limitation and potentiostatic electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Satisfactory results towards the stability of the active species in aqueous media, reasonable discharge capacity with a 0.9 V average voltage and agreeable cycling performance during the charge–discharge process with reproducibility are achieved. For the construction of the full cell, the anode material was coupled with LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 as a cathode material.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...