Multiplexing determination of lung cancer biomarkers using electrochemical and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic techniques†
Abstract
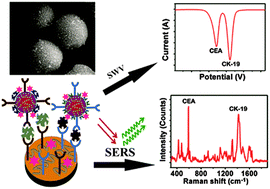
A simple multiplexed electrochemical and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic (SERS) immunosensor is developed for simultaneous detection of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and cytokeratin-19 (CK-19). We find a kind of Raman dye (thionine and Nile blue A)-decorated resin microspheres by π–π stacking interaction, which show both strong SERS signals and electrochemical redox characteristic peaks. Aminosalicylic acid-based resin (AAR) microspheres are synthesized by a template-free method for the first time. The Au nanoparticle (AuNP) coated AAR microspheres (AuNPs/AAR) are prepared by a convenient reduction approach. A sandwich structure contains Raman dye-labeled AuNPs/AAR with the first antibody, the second antibody immobilized on the electrode modified chitosan stabilized AuNPs, and target antigens. Thus, in the presence of the target antigens, the Raman dye-labeled AuNPs/AAR could be bonded to the modified electrode surface by antibody–antigen–antibody interactions. Compared with thionine, Nile blue A has different Raman signals and electrochemical characteristic peaks. As a result, a simultaneous immunoassay for CEA and CK-19 based on multiple labels is developed by using electrochemical and SERS immunoassays. The prepared immunoassay for detection of CEA and CK-19 shows high sensitivity, selectivity, low detection limit and long term stability. The lowest detectable concentration is 0.01 ng mL−1 and 0.04 ng mL−1 for CEA and CK-19 at a signal to noise rate of 3, respectively. The proposed immunosensor can be applied to determine CEA and CK-19 in human blood serum with favorable results. In addition, the electrochemical and SERS immunosensor has potential application in the diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer in the field of clinical research.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...