Discovery of 1,2,4-triazole-1,3-disulfonamides as dual inhibitors of mitochondrial complex II and complex III
Abstract
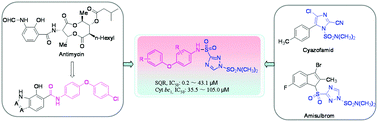
Respiratory chain succinate-ubiquinone oxidoreductase (SQR or complex II) and ubihydroquinone-cytochrome (cyt) c oxidoreductase (cyt bc1 or complex III) have been demonstrated as the promising targets of numerous antibiotics and fungicides. As a continuation of our research work on the development of new fungicides, a series of 1,2,4-triazole-1,3-disulfonamide derivatives with dual functions targeting both SQR and cyt bc1 were designed and synthesized by coupling diverse diphenyl ether moieties with triazolesulfonamide units. These newly synthesized compounds were characterized by elemental analyses, 1H NMR and ESI-MS spectrometry. The in vitro assay indicated that most of the synthesized compounds displayed good inhibition against porcine succinate-cytochrome reductase (SCR) with IC50 values ranging from 3.2 to 81.8 μM, revealing much higher activity than that of the commercial control amisulbrom whose IC50 value is 93.0 μM. Further evaluation against the respective SQR and cyt bc1 indicated that most compounds exhibited SQR-inhibiting activity as well as cyt bc1-inhibiting activity, but the inhibition potency against SQR is much higher than that against cyt bc1, showing that the SCR inhibition might be contributed greatly by the SQR inhibition. The further antibacterial evaluation against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae revealed that four compounds showed excellent potency at the concentration of 20 μg mL−1. In particular, compounds 6h and 6j exhibited much better antibacterial activity than the commercial control bismerthiazol in terms of their EC50. Impressively, 6j has an EC90 of 33.62 μg mL−1, more than 10-fold higher than that of bismerthiazol.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...