S100A4 and its role in metastasis – simulations of knockout and amplification of epithelial growth factor receptor and matrix metalloproteinases†
Abstract
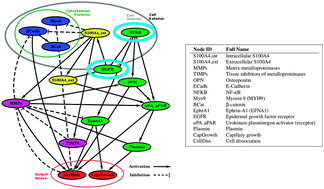
The calcium-binding signalling protein S100A4 enhances metastasis in a variety of cancers. Despite a wealth of data available, the molecular mechanism by which S100A4 drives metastasis is unknown. Integration of the current knowledge defies straightforward intuitive interpretation and requires computer-aided approaches to represent the complexity emerging from cross-regulating species. Here we carried out a systematic sensitivity analysis of the S100A4 signalling network in order to identify key control parameters for efficient therapeutic intervention. Our approach only requires limited details of the molecular interactions and permits a straightforward integration of the available experimental information. By integrating the available knowledge, we investigated the effects of combined inhibition of signalling pathways. Through selective knockout or inhibition of the network components, we show that the interaction between epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and S100A4 modulates the sensitivity of angiogenesis development to matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) activity. We also show that, in cells that express high EGFR, MMP inhibitors are not expected to be useful in tumours if high activity of S100A4 is present.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...