Identifying the causative proteins of similar side effect pairs to explore the common molecular basis of these side effects†
Abstract
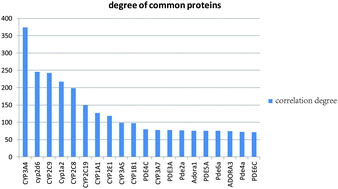
Drug side effects, or adverse drug reactions (ADRs), have become a major public health concern and often cause drug development failure and withdrawal. Some ADRs always occur concomitantly. Therefore, identifying these ADRs and their common molecular basis can better promote their prevention and treatment. In this paper we predicted the potential proteins for ADR pairs with similar mechanisms based on three layers of information: (i) the drug co-occurrence between a pair of ADRs; (ii) the correlation between a protein and an ADR pair based on the co-occurrence of drugs and (iii) the interaction between these proteins within the protein–protein interaction (PPI) network. The methods of randomization and functional annotation are used to investigate and analyze the relation between causative proteins and similar ADR pairs. The prediction accuracy of the relation between similar ADR pairs and related proteins reached 80%, and it increases with the number of drugs shared by the ADR pairs. From the ADR network made of single ADRs from predicted similar ADR pairs, we found that some ADRs are involved in multiple ADR pairs. The functional analysis of these ADR-related proteins suggests that a similar molecular basis is shared by multiple ADR pairs containing the same ADR, and these ADR pairs are almost caused by the same drug sets. The results of this study are reliable and provide a theoretical basis for the better prevention and treatment of ADRs that always occur concomitantly.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...