The study on the material basis and the mechanism for anti-renal interstitial fibrosis efficacy of rhubarb through integration of metabonomics and network pharmacology†
Abstract
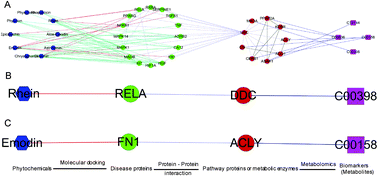
The cooperative material basis of the multi-component and multi-target mechanism of action of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) is difficult to elucidate because of the current lack of appropriate techniques and strategies. In this paper, we focus on rhubarb treatment of renal fibrosis. Molecular docking, metabolic pathway enrichment, and network pharmacology methods were used to theoretically determine the interaction between the components of the rhubarb and disease targets related to renal fibrosis. Moreover, the methods of metabolomics, serum pharmacochemistry, histopathology and immunohistochemistry were used for the model group, the sham-operated group and the rhubarb administration group to reveal the active components and mechanisms of rhubarb. Finally, the experimental and theoretical results were integrated and comprehensively analyzed. Results indicated that anthraquinones and flavanols, such as rhein, emodin, catechin, and epicatechin, were the main active components of rhubarb. These active components play synergistic therapeutic efficacies through regulating the abnormal accumulation of the extracellular matrix, controlling the release of inflammatory factors and maintaining the balance of coagulation and fibrinolysis. Our study showed that the integration of metabolomics and network pharmacology is a powerful strategy for discovering active components of TCMs and for elucidating their mechanisms.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...