Systems biosynthesis of secondary metabolic pathways within the oral human microbiome member Streptococcus mutans†
Abstract
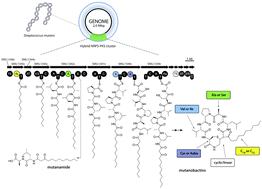
Streptococcus mutans, a Gram-positive human commensal and pathogen, is commonly recognized as a primary causative agent in dental caries. Metabolic activity of this strain results in the creation of acids and secreted products are recognized as pathogenic factors and agents that promote immunomodulation by stimulating the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Products of secondary metabolic pathways of microorganisms from the human microbiome are increasingly investigated for their immunomodulatory functions. In this study, we sought to explore the metabolomic output of nonribosomal peptide pathways within the model S. mutans strain, S. mutans UA159, using a systems metabolomic approach to gain in-depth analysis on products created by this organism and probe these molecules for their immunomodulatory function. Comparative metabolomics and biosynthetic studies using wild-type and nonribosomal peptide deletion strains (within the mutanobactin biosynthetic locus), precursor feedings (fatty acid derivatives) led to the identification of 58 metabolites, 13 of which were structurally elucidated. In addition to these, an assembly line derailment product, mutanamide, was also identified and used to assess immunomodulatory properties of mutanobactins and actions relating to their previously reported functions describing hyphal inhibitory profiles in Candida albicans. The results of this study demonstrate both the complexity and the divergent roles of products stemming from this unique biosynthetic assembly line.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...