Molecular dynamics-based discovery of novel phosphodiesterase-9A inhibitors with non-pyrazolopyrimidinone scaffolds†
Abstract
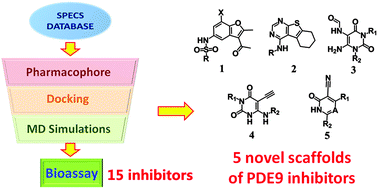
Phosphodiesterase-9A (PDE9A) is a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of diabetes and Alzheimer's disease (AD). The Pfizer PDE9A inhibitor PF-04447943 has completed Phase II clinical trials in subjects with mild to moderate AD in 2013. However, most of the reported PDE9A inhibitors share the same scaffold as pyrazolopyrimidinone, which lacks structural diversity and is unfavorable for the development of novel PDE9A inhibitors. In the present study, a combinatorial method including pharmacophores, molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations, binding free energy calculations, and bioassay was used to discover novel PDE9A inhibitors with new scaffolds rather than pyrazolopyrimidinones from the SPECS database containing about 200 000 compounds. As a result, 15 hits out of 29 molecules (a hit rate of 52%) with five novel scaffolds were identified to be PDE9A inhibitors with inhibitory affinities no more than 50 μM to enrich the structural diversity, different from the pyrazolopyrimidinone-derived family. The high hit ratio of 52% for this virtual screening method indicated that the combinatorial method is a good compromise between computational cost and accuracy. Binding pattern analyses indicate that those hits with non-pyrazolopyrimidinone scaffolds can bind the same active site pocket of PDE9A as classical PDE9A inhibitors. In addition, structural modification of compound AG-690/40135604 (IC50 = 8.0 μM) led to a new one, 16, with an improved inhibitory affinity of 2.1 μM as expected. The five novel scaffolds discovered in the present study can be used for the rational design of PDE9A inhibitors with higher affinities.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...