Pneumatically-actuated artificial cilia array for biomimetic fluid propulsion†
Abstract
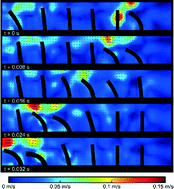
Arrays of beating cilia emerged in nature as one of the most efficient propulsion mechanisms at a small scale, and are omnipresent in microorganisms. Previous attempts at mimicking these systems have foundered against the complexity of fabricating small-scale cilia exhibiting complex beating motions. In this paper, we propose for the first time arrays of pneumatically-actuated artificial cilia that are able to address some of these issues. These artificial cilia arrays consist of six highly flexible silicone rubber actuators with a diameter of 1 mm and a length of 8 mm that can be actuated independently from each other. In an experimental setup, the effects of the driving frequency, phase difference and duty cycle on the net flow in a closed-loop channel have been studied. Net fluid speeds of up to 19 mm s−1 have been measured. Further, it is possible to invert the flow direction by simply changing the driving frequency or by changing the duty cycle of the driving block pulse pressure wave without changing the bending direction of the cilia. Using PIV measurements, we corroborate for the first time existing mathematical models of cilia arrays to measurements on prototypes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...