Imprinted gold 2D nanoarray for highly sensitive and convenient PSA detection via plasmon excited quantum dots†
Abstract
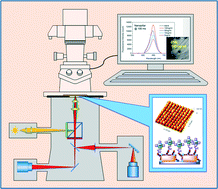
We designed and fabricated two new nanostructured biosensing chips, with which the sensitive detection of prostate specific antigen (PSA) as low as 100 pg ml−1 can be achieved, by measuring the plasmon enhanced fluorescence through a conventional dark field microscope. The gold nanostructure arrays, one with gold nanopillars of 140 nm, the other with gold nanoholes of 140 nm, were fabricated via nanoimprinting onto glass substrate, as localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) generators to enhance the fluorescent emission of fluorophore, e.g. quantum dot (QD). A sandwich bioassay of capture anti-PSA antibody (cAb)/PSA/detection anti-PSA (dAb) labeled by QD-655 was established on the nanostructures, and the perfect LSPR excitation distance (10–15 nm) between the nanostructure and QD-655 was simulated and controlled by a cleft cAb fragment and streptavidin modified QD. QD was chosen in this study due to its photo stability, broad Stokes shift, and long lifetime. As far as we know, this is the first time that QD is applied for PSA detection on the uniform nanostructured sensing chips based on the LSPR enhanced fluorescence. Due to the miniaturized nanoarray sensing chip (1.8 mm × 1.8 mm), the convenience and specificity for the detection of PSA via the sandwich assay, and the high optical detection sensitivity, the platform has great potential for the development of a portable point-of-care (POC) system for outpatient diagnosis and treatment monitoring.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...