Effect of N2 on the emission profile and excitation temperature in axially viewed plasma-ICP OES
Abstract
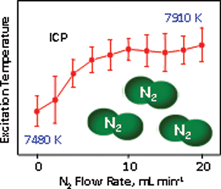
Fundamental studies were conducted in order to gain useful insights about energy transfer that takes place when a low flow (20 mL min−1) of N2 is introduced into the central channel of the Ar-ICP in inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP OES). Axial and radial emission profiles of Mg(I), Mg(II) and Ar(I) were collected along and across the central channels of both Ar-ICP and Ar–N2-ICP. Axial profiles indicated a more energetic plasma close and above the load coil when N2 was added. On the other hand, radial profiles suggested a wider and more uniform central channel with the N2 flow addition. By computing the plasma robustness (Mg(II)/Mg(I) ratio) across the central ICP channel, a low (and uniform) energy coupling was found between the bulk plasma and the central channel of the Ar-ICP, which was significantly improved by adding N2. The results obtained also suggested that N2 plays an important role locally, but does not in the outer regions of the ICP, which in turn denoted an unlikely N2 diffusion. The better excitation conditions caused by N2 were confirmed by measuring the excitation temperature in the central channel of the ICP, using a set of Fe ionic lines, where the excitation temperature increased from 7480 K to 7910 K. The effectiveness of the improved plasma robustness was evaluated for diluted seawater and the results demonstrated that the analyte signal suppression induced by the concomitants was reduced. Accuracy was accessed by analyzing certified reference samples (water and sediment), whereas good agreement among the concentrations found and those certified were observed. These results indicated the absence of spectral interferences caused by N2. The estimated detection limits for both Ar-ICP and Ar–N2-ICP were fairly comparable, revealing that the mixed-gas plasma is a robust source for trace elements determination using axially viewed-ICP OES. It was concluded that addition of a low flow of N2 is a simple way to increase plasma robustness without sacrificing analyte sensitivity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...