Silk fibroin–keratin based 3D scaffolds as a dermal substitute for skin tissue engineering
Abstract
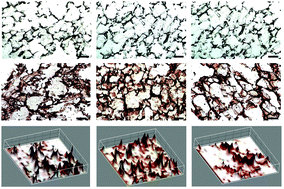
Development of highly vascular dermal tissue-engineered skin substitutes with appropriate mechanical properties and cellular cues is in need for significant advancement in the field of dermal reconstruction. Limitations have been imposed on natural biomaterials despite their superb biocompatibility hence, studies in biomaterial blending have been ongoing. Herein, we investigated blends of silk fibroin and human hair-derived keratin as wound-healing substrates that promote enhanced fibroblast cell adhesion and proliferation. Three-dimensional (3D) blended scaffolds were fabricated by freeze-drying, and their physico-chemical, mechanical and degradable properties were extensively characterized. Cytocompatibility tests observing cell adhesion and cell proliferation have shown significant enhancements in blended scaffolds. Also, its structural composition with high porosity (>85%) and interconnected pores in the range of 100–120 microns further confirms the superiority of the complex compared to its counterparts. FTIR studies identified the enhanced stability within its structure and were followed-up with sequential experiments to demonstrate improved thermal, degradation, and mechanical properties. Furthermore, immunohistochemical staining revealed greater expression of collagen type I in the cultured cells, indicating functional fibroblast proliferation and, hence, the exciting potential of this construct for dermal applications. Taken together, this study demonstrates the promising attributes from blended biomaterials and specifically present silk fibroin and human hair keratin blended scaffolds as a promising dermal substitute for skin tissue engineering.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...