Enzymatic transformation of stevioside using a β-galactosidase from Sulfolobus sp.†
Abstract
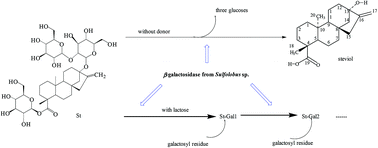
Enzymatic hydrolysis and transgalactosylation of stevioside (St) were investigated using a β-galactosidase from Sulfolobus sp. The hydrolysis yielded steviol as the main final product. Under the optimal transgalactosylation conditions, the highest conversion of stevioside was 87.3% with lactose as a donor, several galactosylated products (St-Gals) were obtained. Metal ions such as Na+, K2+, Ca2+, Ba2+, Mn2+ and Mg2+ (2 mM) did not affect the transgalactosylation activity, while Fe2+, Fe3+ and Cu2+ reduced the transgalactosylation activity of β-galactosidase to 64%, 33% and 18%, respectively.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...