Unraveling the mechanisms of action of lactoferrin-derived antihypertensive peptides: ACE inhibition and beyond
Abstract
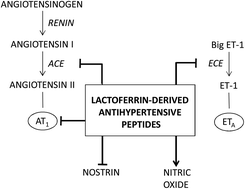
Hypertension is one of the most important causes of cardiovascular and renal morbidity and mortality, and it represents a serious health problem in Western countries. Over the last few decades scientific interest in food-derived antihypertensive peptides has grown as an alternative to drugs in the control of systemic blood pressure. Most of these peptides target the angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) but emerging evidence points to other antihypertensive mechanisms beyond ACE inhibition. The milk protein lactoferrin (LF) is a good source of orally active antihypertensive peptides the characterization of which, including ex vivo functional assays and in vivo approaches, shows that they might act on several molecular targets. This review summarizes the mechanisms of action underlying the blood pressure-lowering effects of LF-derived peptides, focusing on their interaction with different components of the renin-angiotensin (RAS) and endothelin (ET) systems. The ability of LF-derived peptides to modify the expression of genes encoding proteins involved in the nitric oxide (NO) pathway and prostaglandin synthesis is also described.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...