Protective effect of theaflavin-enriched black tea extracts against dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver fibrosis in rats
Abstract
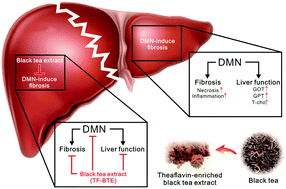
Liver cirrhosis is responsible for hepatic fibrosis resulting in high mortality and is also a risk factor for developing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which is the fifth most common cancer in men and the seventh in women globally. Several studies have found effective anti-cancer activities of theaflavins, the major black tea polyphenols. The objective of this study was to investigate the protective effects of theaflavin-enriched black tea extracts (TF-BTE) on hepatic fibrosis induced by dimethylnitrosamine (DMN) administration in Sprague–Dawley (SD) rats. Treatment of SD rats with DMN (10 mg per kg bw) for 4 weeks produced inflammation and remarkable liver fibrosis assessed by serum biochemistry and histopathological examination. Fibrotic status and the activation of hepatic stellate cells were improved by oral administration of 40% theaflavins in black tea extracts (40% TF-BTE) as evidenced by histopathological examination. Oral administration of 40% TF-BTE at a low dose of 50 mg per kg bw per day and a high dose of 100 mg per kg bw per day attenuated the DMN-induced elevation of serum GOT (glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase) and GPT (glutamic pyruvic transaminase) levels and reduced necrosis, bile duct proliferation, and inflammation. Western blot analyses revealed that TF-BTE inhibited the expression of liver alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) protein. The histochemical examination showed the inhibitory effect of TF-BTE on the p-Smad3 expression. Overall, these data demonstrated that TF-BTE exhibited hepatoprotective effects on experimental fibrosis, potentially by inhibiting the TGF-β1/Smad signaling.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...