Rice bran protein hydrolysates prevented interleukin-6- and high glucose-induced insulin resistance in HepG2 cells
Abstract
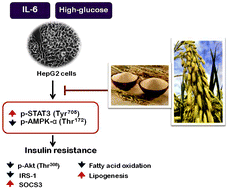
Rice bran, which is a byproduct of rice milling process, contains various nutrients and biologically active compounds. Rice bran protein hydrolysates have various pharmacological activities such as antidiabetic and antidyslipidemic effects. However, there are limited studies about the mechanisms of rice bran protein hydrolysates (RBP) on insulin resistance and lipid metabolism. RBP used in this study were prepared from Thai Jasmine rice. When HepG2 cells were treated with IL-6, the IRS-1 expression and Akt phosphorylation were suppressed. This effect of IL-6 was prevented by RBP in association with inhibition of STAT3 phosphorylation and SOCS3 expression. RBP could increase the phospho-AMPK levels and inhibit IL-6- or high glucose-induced suppression of AMPK and Akt activation. High glucose-induced dysregulation of the expression of lipogenic genes, including SREBP-1c, FASN and CPT-1, was normalized by RBP treatment. Moreover, impaired glucose utilization in insulin resistant HepG2 cells was significantly alleviated by concurrent treatment with RBP. Our results suggested that RBP suppresses inflammatory cytokine signaling and activates AMPK, and thereby these effects may underlie the insulin sensitizing effect.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...