Enhanced bioavailability and safety of curcumagalactomannosides as a dietary ingredient
Abstract
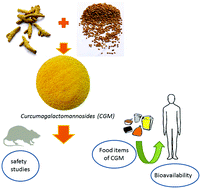
In spite of the various bioavailable formulations of curcumin for pharma and dietary supplement applications, food grade formulations suitable as a dietary ingredient, and capable of providing significant levels of plasma curcumin, are limited. The present contribution describes the safety and oral bioavailability of a novel water soluble formulation of curcumin, curcumagalactomannosides (CGM), when used as a dietary ingredient in selected food items. CGM was prepared using a food grade hydrocolloid (galactomannans) derived from the kitchen spice fenugreek (Trigonella foenum graccum), without using any synthetic excipients. The safety of the formulation was assessed through acute and subchronic toxicity studies on Wistar rats and genotoxicity studies. The efficacy of CGM as a bioavailable dietary ingredient was assessed by successfully preparing various food items and by measuring the post-blood plasma curcumin levels at various time intervals after the consumption of food items. High performance liquid chromatography coupled with a photodiode array detector (HPLC-PDA) and electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometer (ESI-MS/MS) was employed for the quantification of plasma curcuminoids. It was observed that CGM is safe and suitable for further development and clinical studies, with a no observable adverse effect level (NOAEL) up to 2.0 g kg−1 per day b.wt. CGM was found to offer seven to ten times higher bioavailability of curcumin in humans, when incorporated into various food/beverage items at 100 mg CGM per serving size, as compared to the standard unformulated curcumin.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...