Lead removal from solution by a porous ceramisite made from bentonite, metallic iron, and activated carbon†
Abstract
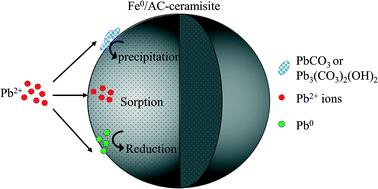
There is increasing interest in using a porous ceramisite as the filter medium for removing heavy metals from wastewater in China given its low cost, easy preparation, large available quantities, high mechanical strength, and good performance to remove various pollutants. In this study, bentonite, metallic iron (Fe0), and activated carbon (AC) were used to prepare a Fe0/AC-ceramisite (diameter 2–4 mm) by sintering at 800 °C in a N2 environment. The Fe0/AC-ceramisite achieved a high Pb2+ removal efficiency (>99%) at ceramisite dosages of 5–10 g L−1, an initial solution pH of 3.0–5.7, and initial Pb2+ concentrations of 50–200 mg L−1. Compared with three control ceramisites including B-ceramisite (made by bentonite only), AC-ceramisite (made by bentonite and AC), and Fe0-ceramisite (made by bentonite and Fe0), the enhanced Pb2+ removal by the Fe0/AC-ceramisite was mainly attributed to the iron–carbon micro-electrolysis induced by the addition of AC. A first-order kinetics model fit well for the Pb2+ removal by the Fe0/AC-ceramisite, and the Pb2+ uptake rate increased linearly with the increasing initial solution pH. Results from scanning electron microscopy equipped with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM/EDX), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) indicated that the Pb2+ removal by the Fe0/AC-ceramisite involved multiple mechanisms including sorption, reduction (from Pb2+ to Pb0), and precipitation (in the forms of PbCO3 and Pb3(CO3)2(OH)2).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...