Nonmetal P-doped hematite photoanode with enhanced electron mobility and high water oxidation activity†
Abstract
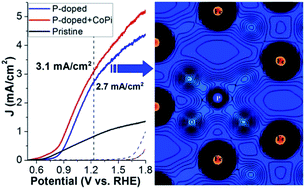
Nonmetal P-doped hematite photoanodes synthesized by a simple impregnation method during the hydrothermal preparation showed remarkable photocurrent densities of 2.3 mA cm−2 and 2.7 mA cm−2 at 1.23 VRHE, for electrodes annealed at 650 °C and 750 °C, respectively. After “Co–Pi” cocatalyst modification, a photocurrent density of over 3 mA cm−2 at 1.23 VRHE could be achieved. The high activity can be attributed to enhanced electron mobility, as verified by DFT + U calculations, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and structural characterizations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...