Centrosymmetric and chiral porous thorium organic frameworks exhibiting uncommon thorium coordination environments†
Abstract
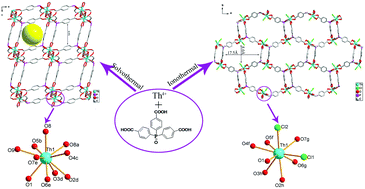
The solvothermal reaction of thorium nitrate and tris-(4-carboxylphenyl)phosphine oxide in DMF affords a centrosymmetric porous thorium organic framework compound [Th(TPO)(OH)(H2O)]·8H2O (1). In contrast, the ionothermal reaction of the same reagents in the ionic liquid 1-butyl-2,3-dimethylimidazolium chloride results in the formation of a rare example of a chiral and porous thorium organic framework compound, [C9H17N2][Th(TPO)Cl2]·18H2O (2), which is derived solely from achiral starting materials. The geometries of the Th(IV) centers in compounds 1 and 2 are both atypical for low valent actinides, which can be best described as a ten-coordinate spherical sphenocorona and an irregular muffin, respectively. A large cavity of 17.5 Å (max. face to face) × 8 Å (min. face to face) with a BET surface area of 623 m2 g−1 in compound 2 is observed. The poor stability indicated by thermal gravimetric analysis and the water-resistance test for compound 2 may be due to the unique anisotropic coordination geometry for thorium. Temperature-dependent luminescence studies for both compounds indicate that the trends in the intensity vary as the Th–Th distance and the coordination environments of Th(IV) centers change.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...