The structures of CyMe4-BTBP complexes of americium(iii) and europium(iii) in solvents used in solvent extraction, explaining their separation properties†
Abstract
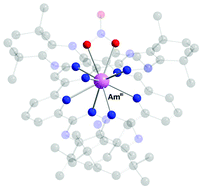
Separation of trivalent actinoid (An(III)) and lanthanoid (Ln(III)) ions is extremely challenging due to their similar ionic radii and chemical properties. Poly-aromatic nitrogen compounds acting as tetradentate chelating ligands to the metal ions in the extraction, have the ability to sufficiently separate An(III) from Ln(III). One of these compounds, 6,6′-bis(5,5,8,8-tetramethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-benzol[1,2,4]triazin-3-yl)[2,2]bipyridine, CyMe4-BTBP, has proven to be resistant towards acidic environments and strong radiation from radioactive decomposition. EXAFS studies of the dicomplexes of CyMe4-BTBP with americium(III) and europium(III) in nitrobenzene, cyclohexanone, 1-hexanol, 1-octanol and malonamide (DMDOHEMA) in 1-octanol have been carried out to get a deeper understanding of the parameters responsible for the separation. The predominating complexes independent of solvent used are [Am(CyMe4-BTBP)2(NO3)]2+ and [Eu(CyMe4-BTBP)2]3+, respectively, which are present as outer-sphere ion-pairs with nitrate ions in the studied solvents with low relative permittivity. The presence of a nitrate ion in the first coordination sphere of the americium(III) complex compensates the charge density of the complex considerably in comparison when only outer-sphere ion-pairs are formed as for the [Eu(CyMe4-BTBP)2]3+ complex. The stability and solubility of a complex in a solvent with low relative permittivity increase with decreasing charge density. The [Am(CyMe4-BTBP)2(NO3)]2+ complex will therefore be increasingly soluble and stabilized over the [Eu(CyMe4-BTBP)2]3+ complex in solvents with decreasing relative permittivity of the solvent. The separation of americium(III) from europium(III) with CyMe4-BTBP as extraction agent will increase with decreasing relative permittivity of the solvent, and thereby also with decreasing solubility of CyMe4-BTBP. The choice of solvent is therefore a balance of a high separation factor and sufficient solubility of the CyMe4-BTBP ligand.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...