Non-aggregated axially disubstituted silicon phthalocyanines bearing electropolymerizable ligands and their aggregation, electropolymerizaton and thermal properties†
Abstract
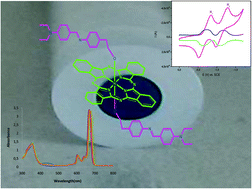
A novel series of axially disubstituted silicon(IV) phthalocyanines bearing electropolymerizable ligands were designed and synthesized for the first time. The silicon(IV) phthalocyanines were characterized by various spectroscopic techniques as well as elemental analysis. The aggregation behavior of the SiPcs were examined in different solvents and at different concentrations in chloroform. In all the studied solvents and concentrations, the SiPcs were non-aggregated. The thermal behavior of the silicon(IV) phthalocyanines was also studied. The electropolymerization properties of the silicon(IV) phthalocyanines were investigated by cyclic and square wave voltammetry. This study is the first example of the electropolymerization of axially disubstituted silicon phthalocyanines. The type of axial ligand on the phthalocyanine ring did not show any effect on the absorption and thermal properties but influenced the electropolymerization of the phthalocyanines.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...