The mechanism of hydrogen evolution in Cu(bztpen)-catalysed water reduction: a DFT study†
Abstract
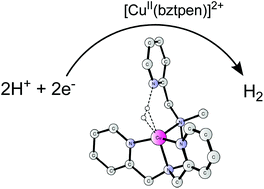
The mechanism of water reduction catalysed by a mononuclear copper complex Cu(bztpen) (bztpen = N-benzyl-N,N′,N′-tris(pyridine-2-ylmethyl)ethylenediamine) has been elucidated by DFT calculations, revealing that hydrogen evolution proceeds via coupling of a Cu(II)-hydride and a pendant pyridinium, and providing important implications for the future design of new catalytic systems for water reduction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...