Ratiometric and colorimetric “naked eye” selective detection of CN− ions by electron deficient Ni(ii) porphyrins and their reversibility studies†
Abstract
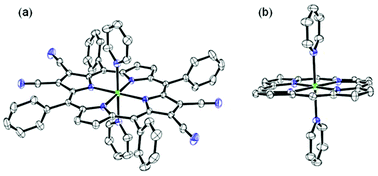
Highly electron deficient β-substituted Ni(II) porphyrins (1–5) were synthesized and utilized as novel sensors for selective rapid visual detection of CN− ions. This article describes the single crystal X-ray structures, electronic spectral and electrochemical redox properties of these sensors. The ratiometric and colorimetric responses of these porphyrins were monitored by the change in optical absorption spectra. These sensors were found to be highly selective for cyanide ions with extremely high binding constants (1016–108 M−2) through axial ligation of CN− ions and are able to detect <0.11 ppm of CN− ions. 1–5 were recovered from 1–5·2CN− adducts by acid treatment and reused without loss of sensing ability. CN− binding strongly perturbs the redox properties of the parent porphyrin π-system. The applicability of 1–5 as practical visible colorimetric test kits for CN− ions in aqueous and non-aqueous media has also been explored. The mode of binding was confirmed by single crystal X-ray, spectroscopic studies and DFT calculations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...