Magnetic colloidal superparticles of Co, Mn and Ni ferrite featured with comb-type and/or linear amphiphilic polyelectrolytes; NMR and MRI relaxometry†
Abstract
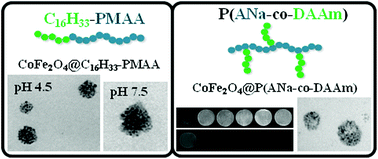
The ability to encapsulate hydrophobic ferrites in colloidal superparticle structures of an a-telechelic hexadecyl-functionalized poly(methacrylic acid) (C16H33-PMAA) polymer with a linear architecture was investigated and compared with that of two amphiphilic comb-type water-soluble copolymers, namely, P(ANa-co-DAAm) and P(MANa-co-DMA), which are comprised of a poly(sodium acrylate) or poly(sodium methacrylate) backbone and pendent dodecyl acrylamide or dodecyl methacrylate chains, respectively. In the case of C16H33-PMAA, the pH-sensitive self-assembly behavior, which was studied through Nile Red probing and TEM, was related to its encapsulation properties. Hydrophobic MFe2O4 nanoparticles coated with oleylamine (MFe2O4@OAm MNPs, where M = Co, Mn, Ni) with a similar shape and size (∼9 nm) and magnetization values of 87.4, 63.1 and 55.0 emu g−1 for CoFe2O4@OAm, MnFe2O4@OAm and NiFe2O4@OAm, respectively, were successfully encapsulated into the hydrophobic cores of spherical micellar structures formed by the copolymers in an aqueous solution through a solvent mixing procedure. The synthesized magnetic colloidal superparticles fell in the static dephasing regime (SDR). NMR relaxivity measurements of MFe2O4@P(ANa-co-DAAm), MFe2O4@P(MANa-co-DMA) and MFe2O4@C16H33-PMAA at pH = 4.5 and pH = 7 (where M = Co, Mn, Ni) at 11.7 T were recorded and the transverse relaxivity (r2) (mM−1 s−1) was determined. Among all, the CoFe2O4@polymers demonstrated the highest r2 relaxivity values, ranging from 61.6 for CoFe2O4@C16H33-PMAA (pH = 7) to 316.0 mM−1 s−1 for CoFe2O4@P(ANa-co-DAAm). The relaxation efficiency (r1 and r2) of CoFe2O4@P(ANa-co-DAAm) was investigated further by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at 1.5 T and 3 T and the r2/r1 ratios were found to be 16.5 and 18.2, respectively, indicating its potential use as a T2 contrast agent.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...