Synthesis and characterization of the new two-dimensional Heisenberg antiferromagnet double perovskite BaLaCuSbO6†
Abstract
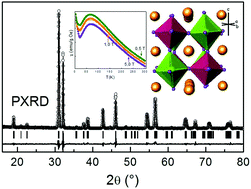
The BaLaCuSbO6 double perovskite has been successfully synthesized by solid state reaction under an air atmosphere. Its structure was refined using powder neutron diffraction in the monoclinic space group I2/m with a 4% antisite disorder on the B cations. Magnetic measurements give signs of 2D-antiferromagnetic behaviour with TN around 64 K. The Jahn–Teller distortion produced by Cu2+ ions favours a crystallographic tetragonal distortion and consequently the in-plane super–superexchange antiferromagnetic interactions, J90°, are favoured over the in-plane J180° antiferromagnetic exchange interactions. Both, J and J′ magnetic interactions have been evaluated according to a Heisenberg antiferromagnetic rectangular model using an approximation to Curie's law in powers of J/T, being |J| around 10 times stronger than |J′|.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Perovskites

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...