Terbium-based time-gated Förster resonance energy transfer imaging for evaluating protein–protein interactions on cell membranes†
Abstract
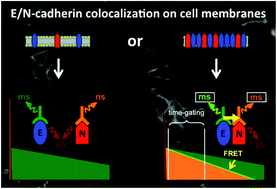
Fluorescence imaging of cells and subcellular compartments is an essential tool to investigate biological processes and to evaluate the development and progression of diseases. In particular, protein–protein interactions can be monitored by Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) between two proximal fluorophores that are attached to specific recognition biomolecules such as antibodies. We investigated the membrane expression of E- and N-cadherins in three different cell lines used as model systems to study epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) and a possible detection of circulating tumour cells (CTCs). EMT is a key process in cancer metastasis, during which epithelial markers (such as E-cadherin) are down-regulated in the primary tumour whereas mesenchymal markers (such as N-cadherin) are up-regulated, leading to enhanced cell motility, intravasation, and appearance of CTCs. Various FRET donor–acceptor pairs and protein recognition strategies were utilized, in which Lumi4-Tb terbium complexes (Tb) and different organic dyes were conjugated to several distinct E- and N-cadherin-specific antibodies. Pulsed excitation of Tb at low repetition rates (100 Hz) and time-gated (TG) imaging of both the Tb-donor and the dye-acceptor photoluminescence (PL) allowed efficient detection of the EMT markers as well as FRET in the case of sufficient donor–acceptor proximity. Efficient FRET was observed only between two E-cadherin-specific antibodies and further experiments indicated that these antibodies recognized the same E-cadherin molecule, suggesting a limited accessibility of cadherins when they are clustered at adherens junctions. The investigated Tb-to-dye FRET systems provided reduced photobleaching compared to the AlexaFluor 488-568 donor–acceptor pair. Our results demonstrate the applicability and advantages of Tb-based TG FRET for efficient and stable imaging of antibody–antibody interactions on different cell lines. They also reveal the limitations of interpreting colocalization on cell membranes in the case of lacking FRET signals.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Dalton Discussion 15: Metal ions in medical imaging


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...