Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 coupled with selective alcohol oxidation under ambient conditions†
Abstract
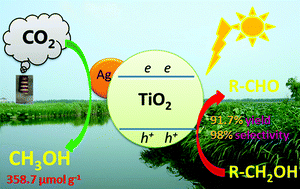
A new method for the reduction of CO2 to CH3OH coupled with selective alcohol oxidation using a photocatalytic method has been developed in the present paper. CO2 as the oxidant was reduced to methanol by photo-induced electrons, and aromatic alcohols were used as the reductants to react with photo-generated holes and were converted to aromatic aldehydes with high selectivity. The maximum conversion of aromatic alcohol to aldehyde was 91.7% with a selectivity of 98%, and the highest yield of methanol was 358.7 μmol g−1. This study could provide a valuable method not only for carbon dioxide conversion into fuel which could remission energy shortages, but also for the selective oxidation of alcohols to produce aldehydes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...