Solvent-free iridium-catalyzed CO2 hydrosilylation: experiments and kinetic modeling†
Abstract
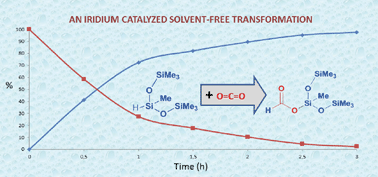
The iridium(III) complex [Ir(H)(CF3SO3)(NSiN)(coe)] (NSiN = bis(pyridine-2-yloxy)methylsilyl, coe = cyclooctene) has been demonstrated to be an active catalyst for the solvent-free hydrosilylation of CO2 with 1,1,1,3,5,5,5-heptamethyltrisiloxane (HMTS) under mild reaction conditions (3 bar). The activity of this catalytic system depends on the reaction temperature. The best catalytic performance has been achieved at 75 °C. A kinetic study at variable temperature (from 25 °C to 75 °C) and constant pressure (3 bar) together with kinetic modeling has been carried out. The results from such a study show an activation energy of 73.8 kJ mol−1 for the process.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...