Carbon-supported gas-cleaning catalysts enable syn gas methanation at atmospheric pressure†
Abstract
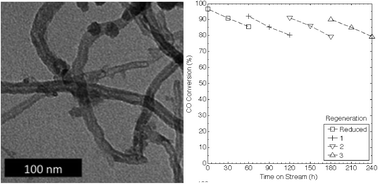
Though feasible for CO methanations in gas-cleaning applications ([CO] < 1%), carbon-nanotube-supported catalysts have never been implemented for the production of synthetic natural gas. To achieve sufficiently active catalysts, NiO particles were grafted onto multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs) using a modified incipient wetness impregnation technique that produced particles ranging from 3 to 18 nm in diameter. The reducibility of the deposited NiO particles was studied, as were the thermal stability and surface area of the composites. The materials were then applied as catalysts for CO methanation in syn gas, where CO concentration is greater than 9%, to synthesise synthetic natural gas (SNG) at atmospheric pressure. Ni/MWNTs containing only 13 wt% Ni catalysed the methanation of CO, achieving ~95% CO conversion and ~85% selectivity for CH4. The factors affecting the activity and stability of the composites were studied, and a method to regenerate the Ni/MWNTs catalyst was developed. Following regeneration, the developed catalysts could be reused with small losses in activity and selectivity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...