Pillared clays as catalysts for methyl parathion removal by advanced oxidation processes
Abstract
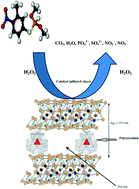
A natural bentonite from Mostaganem in Algeria was modified by intercalation with polyoxocationic solutions (Al·Fe, Al·Co, Al·Cu, Al·Fe·Cu or Al·Fe·La). The modification of the bentonite occurred via pillaring by ionic exchange with these solutions. The addition of these solutions led to the formation of pillared clays with important catalytic properties in environmental impact reactions. The structural and textural properties of materials calcined at 500 °C were determined by several techniques: X-ray fluorescence (XRF), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy and N2 adsorption–desorption analysis. The pillared clays were then used as a Fenton-type heterogeneous catalyst for the heterogeneous sono-Fenton process for the oxidation of methyl parathion in water. The catalytic tests revealed the activity of the introduced iron species and the promoter effect of lanthanide or copper on the catalytic activity of these species. The sono-Fenton method showed promising results for the degradation of methyl parathion when compared with the Fenton method. Therefore, the sono-Fenton method can be a viable alternative technology to the existing methods for treating methyl parathion in wastewater.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...