Micro- and nanogels with labile crosslinks – from synthesis to biomedical applications
Abstract
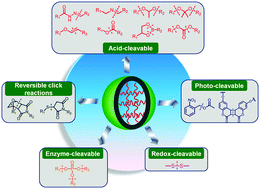
Micro- or nanosized three-dimensional crosslinked polymeric networks have been designed and described for various biomedical applications, including living cell encapsulation, tissue engineering, and stimuli responsive controlled delivery of bioactive molecules. For most of these applications, it is necessary to disintegrate the artificial scaffold into nontoxic residues with smaller dimensions to ensure renal clearance for better biocompatibility of the functional materials. This can be achieved by introducing stimuli-cleavable linkages into the scaffold structures. pH, enzyme, and redox potential are the most frequently used biological stimuli. Moreover, some external stimuli, for example light and additives, are also used to trigger the disintegration of the carriers or their assembly. In this review, we highlight the recent progress in various chemical and physical methods for synthesizing and crosslinking micro- and nanogels, as well as their development for incorporation of cleavable linkages into the network of micro- and nanogels.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...