Intrinsic defects in a photovoltaic perovskite variant Cs2SnI6†
Abstract
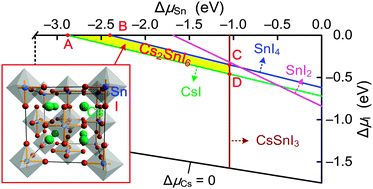
Cs2SnI6, a rarely studied perovskite variant material, is recently gaining a lot of interest in the field of photovoltaics owing to its nontoxicity, air-stability and promising photovoltaic properties. In this work, we report intrinsic defects in Cs2SnI6 using first-principles density functional theory calculations. It is revealed that iodine vacancy and tin interstitial are the dominant defects that are responsible for the intrinsic n-type conduction in Cs2SnI6. Tin vacancy has a very high formation energy (>3.6 eV) due to the strong covalency in the Sn–I bonds and is hardly generated for p-type doping. All the dominant defects in Cs2SnI6 have deep transition levels in the band gap. It is suggested that the formation of deep defects can be suppressed significantly by employing an I-rich synthesis condition, which is inevitable for photovoltaic and other semiconductor applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...