Synthesis and decomposition of Li3Na(NH2)4 and investigations of Li–Na–N–H based systems for hydrogen storage†
Abstract
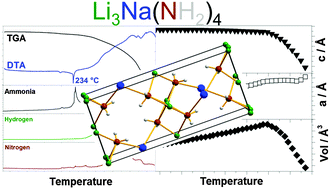
Previous studies have shown modified thermodynamics of amide–hydride composites by cation substitution, while this work systematically investigates lithium–sodium–amide, Li–Na–N–H, based systems. Li3Na(NH2)4 has been synthesized by combined ball milling and annealing of 3LiNH2–NaNH2 with LiNa2(NH2)3 as a minor by-product. Li3+xNa1-x(NH2)4 releases NaNH2 and forms non-stoichiometric Li3+xNa1−x(NH2)4 before it melts at 234 °C, as observed by in situ powder X-ray diffraction. Above 234 °C, Li3+xNa1−x(NH2)4 releases a mixture of NH3, N2 and H2 while a bi-metallic lithium sodium imide is not observed during decomposition. Hydrogen storage performances have been investigated for the composites Li3Na(NH2)4–4LiH, LiNH2–NaH and NaNH2–LiH. Li3Na(NH2)4–4LiH converts into 4LiNH2–NaH–3LiH during mechanochemical treatment and releases 4.2 wt% of H2 in multiple steps between 25 and 340 °C as revealed by Sievert's measurements. All three investigated composites have a lower peak temperature for H2 release as compared to LiNH2–LiH, possibly owing to modified kinetics and thermodynamics, due to the formation of Li3Na(NH2)4 and LiNa2(NH2)3.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...